Board:asus/kgpe-d16: Difference between revisions
(→RAM: Move) |
|||
| Line 234: | Line 234: | ||
=== Miscellaneous Notes === | === Miscellaneous Notes === | ||
The 4 total PCI-e slots may be limiting, but as the board has PCI-e ACS you can install an external ACS supporting PCI-e expansion system and still have IOMMU security, ACS support means that the devices beyond the external switch will be placed in separate IOMMU groups and thus you will maintain security and not have to use the unsafe attachment override for attaching devices to virtual machines. | The 4 total PCI-e slots may be limiting, but as the board has PCI-e ACS you can install an external ACS supporting PCI-e expansion system and still have IOMMU security, ACS support means that the devices beyond the external switch will be placed in separate IOMMU groups and thus you will maintain security and not have to use the unsafe attachment override for attaching devices to virtual machines. | ||
==Fixed issues== | |||
* <strike>Certain DIMMs do not reliably train, leading to slow startup or a reboot loop. The majority of tested DIMMs function normally, however.</strike> Fixed as of coreboot GIT hash 8b9c807 (04/22/2016) | |||
* <strike>RDIMMs do not function on the second slot of a channel (black slots).</strike>Fixed as of coreboot GIT hash 2bb1d30 (04/30/2016) | |||
== FAQ == | == FAQ == | ||
Revision as of 12:14, 3 April 2017
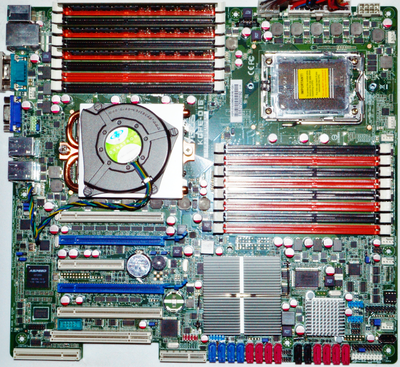
To boot with a second CPU package installed, the 2nd EPS12V connector MUST be connected to a 8-pin power source that has sufficient amperage (Using a converter is risky).
General Information
The KGPE-D16 is a relatively modern AMD Family 10h / 15h motherboard. It is well supported and stable under Coreboot, with all CPUs, RAM, and peripherals functioning normally. Family 10h (61xx) processors do not currently support the isochronous mode required to enable the IOMMU, but Family 15h (62xx, 63xx) processors work well with the IOMMU enabled.
This board is automatically tested by Raptor Engineering's test stand. For more details please visit AutoTest/RaptorEngineering.
A basic system diagram is available in the official manual, which can be downloaded from ASUS directly or from Puget Systems. The diagram is available in Appendix A.1 and has been confirmed to match the hardware shipping from ASUS. Not indicated are the PCIe lane widths for the gigabit network controller, which are both x1. All legacy PCI devices share the same bus, and partially due to this design the SP5100 has severe issues with bridging high-bandwidth PCI peripherals. As such, an external PCI-PCIe bridge is recommended should you need to interface a high bandwidth legacy PCI device to this system; ASMedia controllers have been verified to function correctly.
Northbridge functions are distributed between the CPU internal northbridge and the SR5690 northbridge, which is effectively a HyperTransport to ALink/PCIe translator and switch. There is a separate SP5100 southbridge device, adjacent to the northbridge and residing under the smaller heatsink of the two. This device provides all traditional southbridge services including the LPC bridge and SATA controllers. All southbridge-destined messages, including CPU-originated power state control messages over HyperTransport, pass through the CPU northbridge and are routed to the southbridge via the SR5690 northbridge device.
Incidentally, this design places the IOMMU, which is part of the SR5690, in the correct location to properly shield the main CPU from all unauthorized traffic. If the southbridge connected directly to a HyperTransport link there would be no way to prevent unauthorized DMA from legacy PCI devices connected to the southbridge, or even from the southbridge's embedded microprocessor.
The flash chip is in a PDIP 8 socket (SPI flash chip) on the motherboard.
Respects Your Privacy (RYF) certification
Vikings D16 is a Asus KGPE-D16 board sold with free (de-blobed) a BIOS pre-installed, usually Coreboot. Vikings D16 is the first Respects Your Privacy (RYF) certified board by the Free Software Foundation.<ref>https://www.fsf.org/resources/hw/endorsement/respects-your-freedom</ref>
Installation Notes
- You MUST use at least one real 8PIN EPS12V cable for one CPU, and two real 8PIN EPS12V cables for two CPU's (Adapters may catch fire!)
- coreboot must be flashed externally when migrating from the proprietary BIOS. After coreboot has been flashed and booted at least once, flashrom can safely reprogram the ROM under Linux.
- When migrating from the proprietary BIOS, after flashing coreboot the CMOS memory *must* be cleared. Failing to clear the CMOS will typically result in odd hangs during the boot process.
- Enabling the serial console or EHCI debug console will drastically increase the time needed to boot.
- The proprietary BMC module must be removed for coreboot to function.
- The 63xx "Piledriver" series processors require microcode updates to enable IOMMU (Errata) and may require microcode updates for safe operation due to the 2016 gain-root-via-NMI exploit.
- Fan control is via software with coreboot, you can use fancontrol/pwmconfig to control your 4pin PWM fans - coreboot sets them = 100% at boot-time.
- 12 and 16 core CPU's are split in to two NUMA nodes, memory is divided based on NUMA nodes (1 6282SE 16 core CPU, 2 Nodes, 32GB RAM, 16GB per node)
- Turbo 2 and power saving seems to require a tickless system to function (nohz=on in the kernel cmdline), otherwise the extra cores are always woken up and will never enter CC6.
Features
| Format | SSI-EEB | |
|---|---|---|
| Socket | G34 | |
| Max Processors | 2 | |
| Max RAM | 192GB | Poor hardware design prevents full 256GB - Tpearson |
| PCI-e slots | 4 | 5 physical, 4 concurrent |
| PCI slots | 1 | Via PCI Bridge that also connects onboard AST graphics chip |
| Other Expansion Slots | 1 PIKE | ASUS Proprietary I/O Expansion Slot, Insert PIKE RAID card for second half of the motherboard SATA/SAS ports |
| EEPROM Type | DIP 8 SPI Socket | |
| Factory EEPROM Size | 2MB | |
| Max EEPROM Size | ??? | |
| TPM | YES | With Owner Controlled CRTM - TPM is an option addon module |
| Crossfire XDMA | ??? | Has ACS and dual PCI-e 2.0 x16 slots, so it should work (reported working on vendor bios, need tester for coreboot) |
| Blob Free Operations | YES | |
|---|---|---|
| Native GFX Init | Partial | Text Mode Only - Needs EDID parsing fixed |
| OpenBMC Network KVM Firmware | Soon | See Below |
| HVM | YES | |
|---|---|---|
| SLAT (RVI) | YES | |
| IOMMU | YES | v1.26 with Interrupt Remapping |
| IOMMU for Graphics | YES | Near-Native 3D gaming performance with proper software configuration |
| PCI-e ACS | YES | |
| SR-IOV | ??? | |
| PCI-e ARI | ??? | Required for more than 8 SR-IOV VF per device |
OpenBMC - Network KVM
Raptor Engineering is working on porting OpenBMC to the KGPE-D16 and KCMA-D8 under a crowdfunded contract, it should be done in a few months.
https://www.raptorengineering.com/coreboot/kgpe-d16-bmc-port-offer.php
Note: You will probably require the ASUS ASMB4-iKVM module to use it.
RAM HCL
The following RAM models and configurations have been tested by either Raptor Engineering or a third party and are know to work as of the stated GIT revision. The bolded configuration is automatically tested by Raptor Engineering on every coreboot GIT commit and for most relevant Gerrit changesets; please see the board-status repository for the latest tested GIT hash.
| Manufacturer | Model | Size | Speed | Type | ECC | Populated Slots | CPU | Mainboard | Firmware |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Micron | 36KSF2G72PZ-1G4E1 (N/A) | 16GB | DDR3-1333 | Registered | Yes | A2 / C2 | Opteron 6378 | ASUS KGPE-D16 | Coreboot 2268e0d or later |
| Hynix/Hyundai | HMT151R7BFR4C-H9 | 4GB | DDR3-1333 | Registered | Yes | A2 / C2 | Opteron 6276 | ASUS KGPE-D16 | Libreboot 437619c |
| Kingston | 9965525-055.A00LF | 8GB | DDR3-1600 | Unbuffered | Yes | A2 / C2 / E2 / F2 | Opteron 6328 | ASUS KGPE-D16 | Coreboot 9fba481 |
| Kingston | KVR16R11D4/16 (9965516-483.A00LF) | 16GB | DDR3-1600 | Registered | Yes | All orange slots (128GB) | Opteron 6278/6262HE | ASUS KGPE-D16 | Libreboot 20160907 |
| Kingston | KVR16R11D4K4/64I (9965516-477.A00LF) | 16GB | DDR3-1600 | Registered | Yes | All orange slots (128GB) | Opteron 6278/6262HE/6284SE | ASUS KGPE-D16 | Libreboot 20160907 |
| crucial ("crucial by Micron") | CT16G3ERSLD4160B (MT36KSF2G72PZ-1G6P1NE) | 16GB | DDR3-1600 | Registered | Yes | All orange slots (128GB) | Opteron 6278/6262HE | ASUS KGPE-D16 | Libreboot 20160907 |
Processor Summary
In addition to the 1 or 2 main CPUs, there are no less than three known secondary processors present on the mainboard. All are disabled when running under coreboot.
- There is a very poorly documented microprocessor inside the SR5690; purpose and type unknown. It is believed this processor requires a firmware upload from the main platform firmware or via JTAG in order to start execution.
- A single 8051 processor core is present inside the SB700 southbridge. It normally handles errata related to power states and may also be responsible for the blinking power LED in S3 suspend under the proprietary BIOS. It is believed accesses made by this processor are responsible for the flashrom write failure when the board is booted from the proprietary BIOS. This processor also requires a firmware upload from the main platform firmware or via JTAG in order to start execution.
- The BMC has an integrated ARM core. This is disabled by pin strap when the BMC firmware module is not installed.
Some processors may be present on or activated by add-on modules:
- The optional PIKE add-on cards use ARM cores to handle the SAS protocol, though this firmware is directly loaded from a Flash chip on the module and does not involve any non-local components (e.g. the main CPU never touches the firmware on these modules outside of a manual reflash operation). Raptor Engineering is currently unaware of any SAS controllers that operate without a secondary processor or use libre firmware; the protocol is simply too complex to handle via a mask ROM, and as there are only one or two suppliers of SAS controllers there is very little incentive to release the source code to the firmware. Writing a libre firmware to replace the existing firmware may technically be possible, however it is extremely unlikely this will ever happen due to the man-decades required.
- Installing an ASUS iKVM firmware module will activate the ARM core in the BMC, which has full system access to all peripherals and possibly memory. It is not recommended to use this module as the firmware is both highly privileged and proprietary, and is known to contain at least one critical security bug.
Known Issues
EHCI debug console
The EHCI debug console causes severe USB problems under both Libreboot and coreboot. This typically manifests as very slow boot / slow typing on USB keyboards. This issue appears to extend to the KCMA-D8 and KFSN4-DRE boards as well.
RAM
- Certain hardware revisions of these mainboards appear to contain a bug that leads to a hang in ramstage after cold start, with a varying probability dependent on unknown factors potentially including the debug level, debug output device, and binary Flash layout. Non-affected boards appear to generate an MCE and restart instead of hanging. The hang and/or MCE also appears to be dependent on CPU frequency, with slower CPUs such as the Opteron 6262HE more likely to generate the hang. It is possible, though not confirmed, that the hang is due to generation of an MCE while the SB700 and attached LPC devices are being reconfigured; if this is the case, this would be an unfortunate instance of a hardware bug exposed by coreboot's relatively fast startup.
- Certain models and populations of DIMMs do not function under either coreboot or the proprietary BIOS. These failures may also be contingent on the exact PCB revision and / or CPU model installed. For a list of known failing combinations please visit KGPE-D16 Known Bad Configurations.
256GB of RAM does currently not work
The KGPE-D16 does reportedly not work stably with coreboot and more than 128GB of RAM (this also refers to the RAM modules confirmed working) and would need further work by coreboot developers. MCEs are being reported (the more RAM is used, the more MCEs) and the system eventually crashed.
Tpearson is using this board with 192GB of RAM - "Keep the four slots closest to CPU1 unpopulated (i.e. fill all 8 slots on CPU0, and the 4 farthest from CPU1) and you should have no problems reaching 192GB. Populating all four slots closest to CPU1 with large ECC registered DIMMs is a surefire way to recreate the instability -- note a training failure is not common, the main issue is that the marginal routing causes severe memory corruption when the BKDG-recommended algorithms are used.
PIKE2008 faulty cables
It has been reported that the SATA cables coming with the PIKE2008 cards might be faulty and produce errors like
"%hostname% kernel: mpt2sas_cm0: log_info(0x31120303): originator(PL), code(0x12), sub_code(0x0303)".
Perhaps other production batches are not affected, please leave this note until this is figured out.
Miscellaneous Notes
The 4 total PCI-e slots may be limiting, but as the board has PCI-e ACS you can install an external ACS supporting PCI-e expansion system and still have IOMMU security, ACS support means that the devices beyond the external switch will be placed in separate IOMMU groups and thus you will maintain security and not have to use the unsafe attachment override for attaching devices to virtual machines.
Fixed issues
Certain DIMMs do not reliably train, leading to slow startup or a reboot loop. The majority of tested DIMMs function normally, however.Fixed as of coreboot GIT hash 8b9c807 (04/22/2016)RDIMMs do not function on the second slot of a channel (black slots).Fixed as of coreboot GIT hash 2bb1d30 (04/30/2016)
FAQ
CPU's sold by AMD
| Processor | Part Number | Cores | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Opteron 6386 SE | OS6386YETGGHK | 16 | Best, but "Piledriver" CPU's require microcode updates for secure operation and IOMMU |
| Opteron 6284 SE | ecx-Off-US-917385 | 16 | Second best |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_AMD_Opteron_microprocessors